Page 259 - Interp Book
P. 259
No.
No. Ground
Original truth
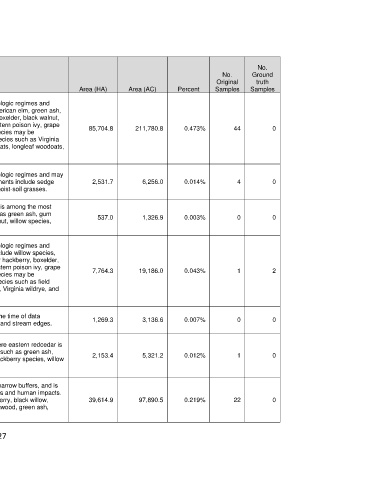
Mapped Type Name Brief Description Area (HA) Area (AC) Percent Samples Samples
This type is mapped on bottomland soils across a variety of hydrologic regimes and
various stages of disturbance. Common tree species include American elm, green ash,
bur oak, sugar hackberry, slippery elm, black willow, sycamore, boxelder, black walnut,
Southeastern Great Shumard oak, western soapberry, and pecan. Vines such as eastern poison ivy, grape
Plains: Bottomland species, peppervine species, Virginia creeper, and greenbriar species may be 85,704.8 211,780.8 0.473% 44 0
Hardwood Forest
conspicuous components. Herbaceous species many include species such as Virginia
wildrye, Bermudagrass, Johnsongrass, field brome, Indian woodoats, longleaf woodoats,
and sedge species.
Southeastern Great This type is mapped on bottomland soils across a variety of hydrologic regimes and may
Plains: Bottomland circumscribe a variety of herbaceous wetlands. Common components include sedge 2,531.7 6,256.0 0.014% 4 0
Herbaceous Wetland and rush species, spikerush species, cattails, smartweeds, and moist-soil grasses.
Southeastern Great This type is mapped on bottomland soils where eastern redcedar is among the most
Plains: Bottomland important species. Other components may include species such as green ash, gum 537.0 1,326.9 0.003% 0 0
Mixed Evergreen - bumelia, possumhaw, honeylocust, hackberry species, black walnut, willow species,
Hardwood Forest Osage orange, and elm species.
This type is mapped on bottomland soils across a variety of hydrologic regimes and
various stages of disturbance. Common shrubs or small trees include willow species,
Southeastern Great common buttonbush, green ash, winged elm, gum bumelia, sugar hackberry, boxelder,
Plains: Bottomland possumhaw, honeylocust, and Osage orange. Vines such as eastern poison ivy, grape 7,764.3 19,186.0 0.043% 1 2
Shrubland and species, peppervine species, Virginia creeper, and greenbriar species may be
Young Woodland conspicuous components. Herbaceous species many include species such as field
brome, Bermudagrass, little barley, cheatgrass, western ragweed, Virginia wildrye, and
sedge species.
Southeastern Great These areas were essentially unvegetated during all seasons at the time of data
Plains: Riparian acquisition (circa 2012), and may represent river-scoured islands and stream edges. 1,269.3 3,136.6 0.007% 0 0
Barrens
Southeastern Great This type is mapped on bottomland soils circumscribes areas where eastern redcedar is
Plains: Riparian the prevailing dominant. Other components may include species such as green ash,
Eastern Redcedar gum bumelia, Osage orange, honeylocust, western soapberry, hackberry species, willow 2,153.4 5,321.2 0.012% 1 0
Woodland and species, and elm species.
Shrubland
This type is mapped along first and second order streams within narrow buffers, and is
Southeastern Great represented by vegetation influenced by a variety of water regimes and human impacts.
Plains: Riparian The corridors may be dominated by species such as sugar hackberry, black willow, 39,614.9 97,890.5 0.219% 22 0
Hardwood Woodland pecan, slippery elm, green ash, post oak, sycamore, plains cottonwood, green ash,
boxelder, Osage orange, or western soapberry.
227