Page 229 - Interp Book
P. 229
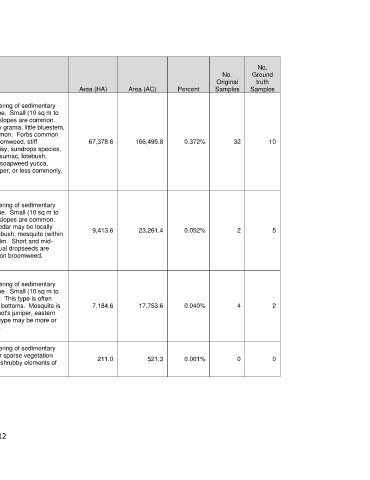
No.
No. Ground
Original truth
Mapped Type Name Brief Description Area (HA) Area (AC) Percent Samples Samples
This type is mapped in broken landscapes associated with weathering of sedimentary
rocks where patches or layers of gyp are common in the landscape. Small (10 sq m to
200 sq m), open, sparsely vegetated patches or layers of gyp on slopes are common.
Short and mid-grasses such as sideoats grama, blue grama, hairy grama, little bluestem,
cane bluestem, sand dropseed, and annual bromes are also common. Forbs common
Canyon: Gyp in the modern landscape include broom snakeweed, common broomweed, stiff 67,378.6 166,495.8 0.372% 32 10
Grassland
greenthread, Navajo tea, Indian breadroot, stemmy four-nerve daisy, sundrops species,
and western ragweed. Important shrubs may include skunkbush sumac, lotebush,
mesquite (within range), and Mohr shin oak. Succulents such as soapweed yucca,
pricklypear, and Christmas cactus may be present. Pinchot's juniper, or less commonly,
eastern redcedar may be present.
This type is mapped in broken landscapes associated with weathering of sedimentary
rocks where patches or layers of gyp are common in the landscape. Small (10 sq m to
200 sq m), open, sparsely vegetated patches or layers of gyp on slopes are common.
Canyon: Gyp Juniper Pinchot's juniper is the most common dominant, but eastern redcedar may be locally
Shrubland important. Other woody species may include sumac species, lotebush, mesquite (within 9,413.6 23,261.4 0.052% 2 5
range), soapberry, sugar hackberry, gum bumelia, and Siberian elm. Short and mid-
grasses such as gramas, little bluestem, cane bluestem, and annual dropseeds are
important, along with forbs such as broom snakeweed and common broomweed.
This type is mapped in broken landscapes associated with weathering of sedimentary
rocks where patches or layers of gyp are common in the landscape. Small (10 sq m to
Canyon: Gyp 200 sq m), open, sparsely vegetated patches of gyp are common. This type is often 7,184.6 17,753.6 0.040% 4 2
mapped low on the landscape at the base of slopes or on canyon bottoms. Mesquite is
Mesquite Shrubland
the most common dominant, and species such as lotebush, Pinchot's juniper, eastern
redcedar, soapberry, and sugar hackberry may be present. This type may be more or
less open, with elements of the Canyon: Gyp Grassland common.
This type is mapped in broken landscapes associated with weathering of sedimentary
Canyon: Gyp rocks where patches of open gyp with bare rock or bare ground or sparse vegetation 211.0 521.3 0.001% 0 0
Sparsely Vegetated occur over fairly extensive areas (>1000 sq m). Herbaceous and shrubby elements of
other Canyon: Gyp types may be present.
212