Page 239 - Interp Book
P. 239
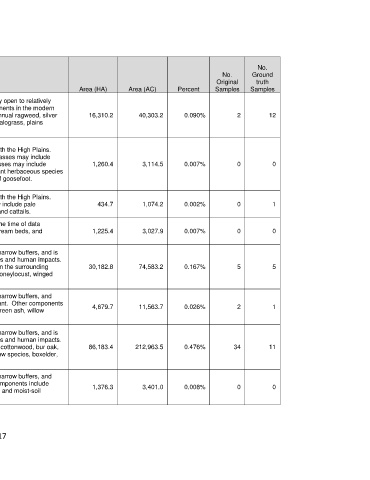
No.
No. Ground
Original truth
Mapped Type Name Brief Description Area (HA) Area (AC) Percent Samples Samples
This type is mapped over bottomland soils and is characterized by open to relatively
dense stands of mesquite in grazed grasslands. Common components in the modern
High Plains: landscape include field brome, cheatgrass, prairie broomweed, annual ragweed, silver 16,310.2 40,303.2 0.090% 2 12
Mesquite Shrubland bluestem, sideoats grama, blue grama, other grama species, buffalograss, plains
pricklypear, and little bluestem.
Playas are closed, internally drained basins, mainly associated with the High Plains.
Vegetation varies over time with moisture. Common dominant grasses may include
High Plains: Playa buffalograss, western wheatgrass, and vine mesquite. Other grasses may include 1,260.4 3,114.5 0.007% 0 0
Grassland
tumblegrass, foxtail barley, and annual rabbitsfoot grass. Important herbaceous species
may include povertyweed, annual saltmarsh aster, and narrowleaf goosefoot.
Playas are closed, internally drained basins, mainly associated with the High Plains.
High Plains: Playa Vegetation varies over time with moisture. Common species may include pale 434.7 1,074.2 0.002% 0 1
Marsh
spikerush, hairy waterclover, flatsedges, knotweeds, wedgeleaf, and cattails.
These areas were essentially unvegetated during all seasons at the time of data
High Plains: Riparian acquisition (circa 2012), and may represent stream scours, dry stream beds, and 1,225.4 3,027.9 0.007% 0 0
Barrens
exposed rock.
This type is mapped along first and second order streams within narrow buffers, and is
represented by vegetation influenced by a variety of water regimes and human impacts.
High Plains: Riparian This type may represent slightly moister or much wetter types than the surrounding 30,182.8 74,583.2 0.167% 5 5
Deciduous Shrubland
uplands. Common species include willow species, winged elm, honeylocust, winged
soapberry, sugar hackberry, ash species, and elm species.
High Plains: Riparian This type is mapped along first and second order streams within narrow buffers, and
Eastern Redcedar consists of areas where eastern redcedar is the prevailing dominant. Other components 4,679.7 11,563.7 0.026% 2 1
Woodland and may include winged elm, winged soapberry, hackberry species, green ash, willow
Shrubland species, and elm species.
This type is mapped along first and second order streams within narrow buffers, and is
represented by vegetation influenced by a variety of water regimes and human impacts.
High Plains: Riparian A wide variety of canopy trees may be important, including plains cottonwood, bur oak, 86,183.4 212,963.5 0.476% 34 11
Hardwood Woodland
sycamore, winged soapberry, Siberian elm, sugar hackberry, willow species, boxelder,
elm species, gum bumelia, ash species, and honeylocust.
This type is mapped along first and second order streams within narrow buffers, and
High Plains: Riparian may circumscribe a variety of herbaceous wetlands. Common components include 1,376.3 3,401.0 0.008% 0 0
Herbaceous Wetland sedge and rush species, spikerush species, cattails, smartweeds, and moist-soil
grasses.
217