Page 235 - Interp Book
P. 235
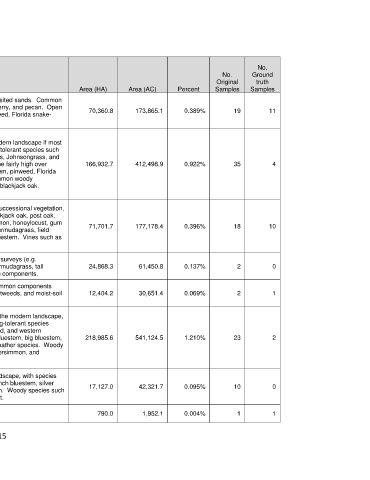
No.
No. Ground
Original truth
Mapped Type Name Brief Description Area (HA) Area (AC) Percent Samples Samples
Crosstimbers: This type is mapped over more or less deep, wind- or water-deposited sands. Common
Sandyland Post Oak trees include post oak, blackjack oak, black hickory, sugar hackberry, and pecan. Open 70,360.8 173,865.1 0.389% 19 11
- Blackjack Oak stands may include herbaceous cover with species such as pinweed, Florida snake-
Forest and Woodland cotton, southern jointweed, and Alabama supplejack.
This type is mapped over more or less deep sands and in the modern landscape if most
often represented by grazed pasture with non-native and grazing-tolerant species such
Crosstimbers: as Bermudagrass, tall fescue, annual ragweed, weeping lovegrass, Johnsongrass, and
Sandyland Shrubland sandbur species. Overall herbaceous species diversity tends to be fairly high over 166,932.7 412,498.9 0.922% 35 4
and Grassland deeper sand, and some may contain species such as little bluestem, pinweed, Florida
snake-cotton, southern jointweed, and Alabama supplejack. Common woody
components include Chickasaw plum, post oak, winged elm, and blackjack oak.
This type represents pastures and woodland edges with sparse successional vegetation,
Crosstimbers: Young including shrubs and trees. Common woody species include blackjack oak, post oak,
winged elm, sumac species, hackberry species, common persimmon, honeylocust, gum
Post Oak - Blackjack bumelia, and pecan. Herbaceous areas have species such as Bermudagrass, field 71,701.7 177,178.4 0.396% 18 10
Oak Woodland
brome, tall fescue, purpletop tridens, little bluestem, and silver bluestem. Vines such as
eastern poison ivy and greenbriar species are common.
This type is mapped over soils defined as disturbed by digital soil surveys (e.g.
Disturbed Soil slickspots, pits). Non-native and disturbance species such as Bermudagrass, tall 24,868.3 61,450.8 0.137% 2 0
Pasture
fescue, Johnsongrass, winged elm, and honeylocust are common components.
This type circumscribes all varieties of herbaceous wetlands. Common components
Eastern Great Plains: include sedge and rush species, spikerush species, cattails, smartweeds, and moist-soil 12,404.2 30,651.4 0.069% 2 1
Herbaceous Wetland
grasses.
This type occurs mainly over unbroken sod in grazed pastures in the modern landscape,
but some native hay meadows are also present. Common grazing-tolerant species
include field brome, tall fescue, silver bluestem, prairie broomweed, and western
Flint Hills: Tallgrass (Cuman) ragweed. Tallgrass prairie elements may include little bluestem, big bluestem, 218,985.6 541,124.5 1.210% 23 2
Prairie/Pasture
switchgrass, heath aster, leadplant, Canada goldenrod, and gayfeather species. Woody
plants such as eastern redcedar, honeylocust, pecan, common persimmon, and
Chickasaw plum may be present.
This type is mainly grazed or improved pasture in the modern landscape, with species
Grand Prairie: such as Bermudagrass, prairie broomweed, field brome, King Ranch bluestem, silver
Prairie/Pasture bluestem, western (Cuman) ragweed, and Johnsongrass common. Woody species such 17,127.0 42,321.7 0.095% 10 0
as winged elm, Chickasaw plum, and honeylocust may be present.
High Plains: Active This type consists of bare dunes with little vegetation. 790.0 1,952.1 0.004% 1 1
Sand Dunes
215