Page 237 - Interp Book
P. 237
No.
No. Ground
Original truth
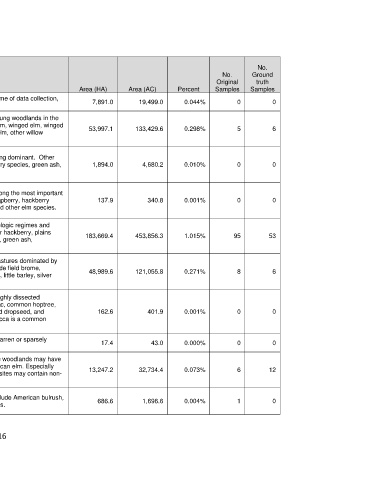
Mapped Type Name Brief Description Area (HA) Area (AC) Percent Samples Samples
High Plains: This type consists of areas that were largely unvegetated at the time of data collection, 7,891.0 19,499.0 0.044% 0 0
Bottomland Barrens including sand bars, mud flats, and bare rock in bottoms.
This type is mainly represented by successional shrublands or young woodlands in the
High Plains: modern landscape. Species such as black willow, Chickasaw plum, winged elm, winged
Bottomland soapberry, plains cottonwood, green ash, honeylocust, Siberian elm, other willow 53,997.1 133,429.6 0.298% 5 6
Deciduous Shrubland
species, and other elm species may be present.
High Plains: This type consists of areas where eastern redcedar is the prevailing dominant. Other
Bottomland Eastern components may include winged elm, winged soapberry, hackberry species, green ash, 1,894.0 4,680.2 0.010% 0 0
Redcedar Woodland willow species, and other elm species.
and Shrubland
High Plains: This type is represented by stands where eastern redcedar is among the most important
Bottomland species. Other components may include winged elm, winged soapberry, hackberry 137.9 340.8 0.001% 0 0
Hardwood - Eastern species, green ash, honeylocust, Siberian elm, willow species, and other elm species.
Redcedar Forest
This type is mapped on bottomland soils across a variety of hydrologic regimes and
High Plains: various stages of disturbance. Typical canopy trees include sugar hackberry, plains
Bottomland cottonwood, bur oak, western soapberry, boxelder, American elm, green ash, 183,669.4 453,856.3 1.015% 95 53
Hardwood Forest
honeylocust, Siberian elm, and pecan.
This type in the modern landscape consists primarily of grazed pastures dominated by
High Plains: non-native or grazing-tolerant species. Typical components include field brome,
Bottomland Bermudagrass, prairie broomweed, western ragweed, cheatgrass, little barley, silver 48,989.6 121,055.8 0.271% 8 6
Herbaceous Wetland bluestem, grama species, buffalograss, and little bluestem.
This rare type was mapped mainly in canyons of Black Mesa in highly dissected
landscapes. Important woody species may include fragrant sumac, common hoptree,
High Plains: Canyon mountain mahogany, and one-seed juniper. Grama species, sand dropseed, and 162.6 401.9 0.001% 0 0
Deciduous Shrubland
James' galleta may occur in the herbaceous layer. Soapweed yucca is a common
succulent.
High Plains: Canyon This rare type was mapped in canyons of Black Mesa that were barren or sparsely 17.4 43.0 0.000% 0 0
Sparsely Vegetated vegetation, and is represented by bare slopes and rock outcrops.
This type is mapped over aeolian and alluvial deep sands. These woodlands may have
High Plains: Deep species such as western soapberry, netleaf hackberry, and American elm. Especially 13,247.2 32,734.4 0.073% 6 12
Sand Woodland near drainages, eastern cottonwood may be conspicuous. Some sites may contain non-
natives such as Siberian elm and black locust.
High Plains: This type represents emergent marsh. Common species may include American bulrush,
Depression Torrey's rush, pale spikerush, flatsedges, cattails, and smartweeds. 686.6 1,696.6 0.004% 1 0
Herbaceous Wetland
216