Page 35 - Interp Book
P. 35
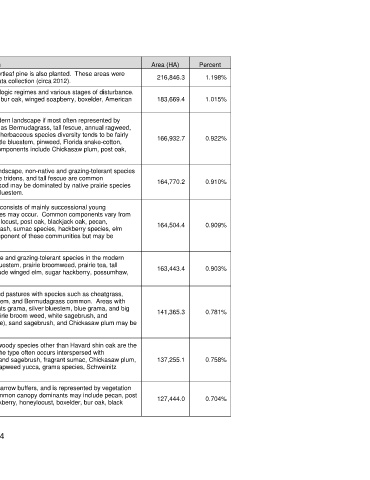
Mapped Type Name Brief Description Area (HA) Percent
This type consists mainly of loblolly pine plantations, although shortleaf pine is also planted. These areas were
Pine Plantation 216,846.3 1.198%
mature enough to be dominated by pines at the time of satellite data collection (circa 2012).
High Plains: This type is mapped on bottomland soils across a variety of hydrologic regimes and various stages of disturbance.
Bottomland Typical canopy trees include sugar hackberry, plains cottonwood, bur oak, winged soapberry, boxelder, American 183,669.4 1.015%
Hardwood Forest elm, green ash, honeylocust, Siberian elm, pecan, and soapberry.
This type is mapped over more or less deep sands and in the modern landscape if most often represented by
Crosstimbers: grazed pasture with non-native and grazing-tolerant species such as Bermudagrass, tall fescue, annual ragweed,
Sandyland weeping lovegrass, Johnsongrass, and sandbur species. Overall herbaceous species diversity tends to be fairly 166,932.7 0.922%
Shrubland and high over deeper sand, and some may contain species such as little bluestem, pinweed, Florida snake-cotton,
Grassland southern jointweed, and Alabama supplejack. Common woody components include Chickasaw plum, post oak,
winged elm, and blackjack oak.
This type circumscribes a variety of grasslands. In the modern landscape, non-native and grazing-tolerant species
Arkansas Valley: such as Bermudagrass, field brome, marsh bristlegrass, thickspike tridens, and tall fescue are common 164,770.2 0.910%
Prairie/Pasture components. Some native hay meadows or lightly grazed native sod may be dominated by native prairie species
such as little bluestem, switchgrass, yellow Indiangrass, and big bluestem.
This type is mapped on prairie soils across much of the state and consists of mainly successional young
woodlands or shrublands, although some more natural communities may occur. Common components vary from
Ruderal Deciduous region to region, and may include honeylocust, winged elm, black locust, post oak, blackjack oak, pecan,
Shrubland and Chickasaw plum, western soapberry, common persimmon, green ash, sumac species, hackberry species, elm 164,504.4 0.909%
Young Woodland
species, and Osage orange. Eastern redcedar is not a major component of these communities but may be
present.
This type is mainly represented by grazed pastures with non-native and grazing-tolerant species in the modern
West Gulf Coastal landscape. Common species may include Bermudagrass, little bluestem, prairie broomweed, prairie tea, tall 163,443.4 0.903%
Plain: Pasture fescue, field brome, and Johnsongrass. Woody species may include winged elm, sugar hackberry, possumhaw,
green ash, and eastern redcedar.
In the modern landscape, this type is mainly represented by grazed pastures with species such as cheatgrass,
western ragweed, sand dropseed, field brome, King Ranch Bluestem, and Bermudagrass common. Areas with
Central Mixedgrass: less grazing pressure have species such as little bluestem, sideoats grama, silver bluestem, blue grama, and big
Sandy bluestem. Other common species include snake broomweed, prairie broom weed, white sagebrush, and 141,365.3 0.781%
Prairie/Pasture
soapweed yucca. Eastern redcedar, honey mesquite (within range), sand sagebrush, and Chickasaw plum may be
present.
This type is mapped over aeolian and alluvial deep sands where woody species other than Havard shin oak are the
prevailing dominants, although it may be present, within range. The type often occurs interspersed with
High Plains: Sandhill grasslands. Common species in the modern landscape include sand sagebrush, fragrant sumac, Chickasaw plum, 137,255.1 0.758%
Shrubland
sand bluestem, sand dropseed, cheatgrass, western ragweed, soapweed yucca, grama species, Schweinitz
flatsedge, yellow sundrops, and annual buckwheat.
This type is mapped along first and second order streams within narrow buffers, and is represented by vegetation
South Central influenced by a variety of water regimes and human impacts. Common canopy dominants may include pecan, post
Interior: Riparian oak, Shumard oak, green ash, slippery elm, sycamore, sugar hackberry, honeylocust, boxelder, bur oak, black 127,444.0 0.704%
Hardwood Woodland willow, and American elm.
24