Page 36 - Interp Book
P. 36
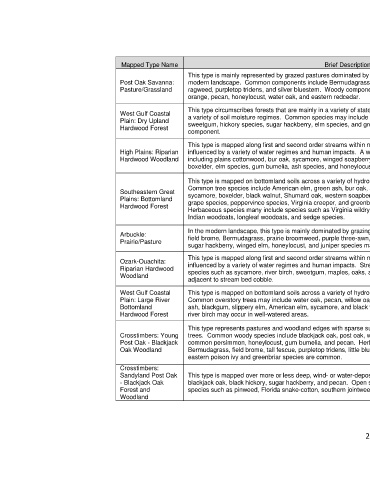
Mapped Type Name Brief Description Area (HA) Percent
This type is mainly represented by grazed pastures dominated by non-native and grazing-tolerant species in the
Post Oak Savanna: modern landscape. Common components include Bermudagrass, field brome, tall fescue, western (Cuman) 119,156.2 0.658%
Pasture/Grassland ragweed, purpletop tridens, and silver bluestem. Woody components may include post oak, winged elm, Osage
orange, pecan, honeylocust, water oak, and eastern redcedar.
This type circumscribes forests that are mainly in a variety of states of recovery from human disturbance, and over
West Gulf Coastal a variety of soil moisture regimes. Common species may include white oak, southern red oak, post oak, water oak,
Plain: Dry Upland sweetgum, hickory species, sugar hackberry, elm species, and green ash. Loblolly or shortleaf pine may be a 90,260.9 0.499%
Hardwood Forest
component.
This type is mapped along first and second order streams within narrow buffers, and is represented by vegetation
High Plains: Riparian influenced by a variety of water regimes and human impacts. A wide variety of canopy trees may be important, 86,183.4 0.476%
Hardwood Woodland including plains cottonwood, bur oak, sycamore, winged soapberry, Siberian elm, sugar hackberry, willow species,
boxelder, elm species, gum bumelia, ash species, and honeylocust.
This type is mapped on bottomland soils across a variety of hydrologic regimes and various stages of disturbance.
Common tree species include American elm, green ash, bur oak, sugar hackberry, slippery elm, black willow,
Southeastern Great sycamore, boxelder, black walnut, Shumard oak, western soapberry, and pecan. Vines such as eastern poison ivy,
Plains: Bottomland grape species, peppervince species, Virginia creeper, and greenbriar species may be conspicuous components. 85,704.8 0.473%
Hardwood Forest
Herbaceous species many include species such as Virginia wildrye, Bermudagrass, Johnsongrass, field brome,
Indian woodoats, longleaf woodoats, and sedge species.
In the modern landscape, this type is mainly dominated by grazing-tolerant native or non-native species such as
Arbuckle: field brome, Bermudagrass, prairie broomweed, purple three-awn, and silver bluestem. Woody species such as 82,776.9 0.457%
Prairie/Pasture
sugar hackberry, winged elm, honeylocust, and juniper species may be components.
This type is mapped along first and second order streams within narrow buffers, and is represented by vegetation
Ozark-Ouachita: influenced by a variety of water regimes and human impacts. Stream gradient tends to be relatively high, and
Riparian Hardwood species such as sycamore, river birch, sweetgum, maples, oaks, and hazel alder may grow near steep banks or 79,975.7 0.442%
Woodland
adjacent to stream bed cobble.
West Gulf Coastal This type is mapped on bottomland soils across a variety of hydrologic regimes and various stages of disturbance.
Plain: Large River Common overstory trees may include water oak, pecan, willow oak, sugar hackberry, post oak, sweetgum, green 72,711.3 0.402%
Bottomland ash, blackgum, slippery elm, American elm, sycamore, and black willow. Shrubs such as common buttonbush and
Hardwood Forest river birch may occur in well-watered areas.
This type represents pastures and woodland edges with sparse successional vegetation, including shrubs and
Crosstimbers: Young trees. Common woody species include blackjack oak, post oak, winged elm, sumac species, hackberry species,
Post Oak - Blackjack common persimmon, honeylocust, gum bumelia, and pecan. Herbaceous areas have species such as 71,701.7 0.396%
Oak Woodland Bermudagrass, field brome, tall fescue, purpletop tridens, little bluestem, and silver bluestem. Vines such as
eastern poison ivy and greenbriar species are common.
Crosstimbers:
Sandyland Post Oak This type is mapped over more or less deep, wind- or water-deposited sands. Common trees include post oak,
- Blackjack Oak blackjack oak, black hickory, sugar hackberry, and pecan. Open stands may include herbaceous cover with 70,360.8 0.389%
Forest and species such as pinweed, Florida snake-cotton, southern jointweed, and Alabama supplejack.
Woodland
25