Description
The mountain lion can be identified by several distinguishing characteristics. Its tail is more than half the length of the body, it has black tips on the tail and ears, and is primarily tan in color.
Confirmed Sightings Mountain Lions in Oklahoma
The mountain lion is one of Oklahoma's most elusive and discussed wildlife species. “Do we have mountain lions here or not?” Oklahoma has far fewer mountain lions than rumors would lead you to believe. Though most confirmed reports are thought to be of transient individuals, the Wildlife Department confirmed two separate mountain lions observed with kittens in different regions of the state in 2024. Although mountain lions, sometimes called cougars, pumas, panthers, painters, or catamounts, were common in Oklahoma and elsewhere in the Plains prior to European settlement, they were eradicated during the 19th century.
As the countryside was settled and developed, the large predators were shot. People also killed almost all of the deer, the mountain lions’ primary food source. Sightings and evidence of cougars have been documented back to 1852, where two cougars were killed in southwest Oklahoma. Accounts continued into 1953 when an Oklahoma State University mammalogist documented tracks of a mountain lion southeast of Canton Lake in northwest Oklahoma. Further reports continued into September of 1984, where the refuge manager observed a mountain lion on the Wichita Mountains Wildlife Refuge. In 1957, the Oklahoma Department of Wildlife Conservation listed the mountain lion as a game species with a closed season.
One thing is certain, despite many rumors and claims to the contrary. ODWC has never stocked, relocated or released any mountain lions in the state of Oklahoma. Furthermore the agency has no plans to do so. Because mountain lions are reclusive animals, it's hard to know exactly when and where they are present. As compelling as a reported sighting may be, we must gather hard evidence before we can say, “yes, we have a confirmed mountain lion sighting.” Although hundreds of recorded sightings have been reported each year, a small percentage have yielded enough physical evidence to clearly confirm the presence of a mountain lion.
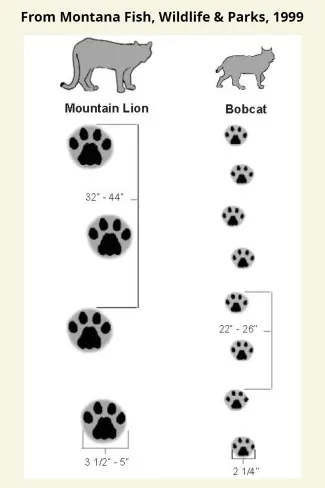
What about the hundreds of others? Some turned out to be different animals. Bobcats and house cats – along with domestic dogs, coyotes, foxes, deer, and even rabbits – have also been mistaken for mountain lions. With some sightings, there just isn’t enough physical evidence (hair, scat, tracks, photos, etc.) to confirm or deny a mountain lion was there.
In the areas of every documented population in the United States, biologists are able to locate numerous tracks, prey kills, scrapes (made when lions scent-mark their territories), and photos, which are often available from the many motion-detecting game cameras that hunters use to monitor trails. Also, frequent mountain lion road-kills turn up, of all ages and of both sexes. The nearest established populations to Oklahoma are in Texas, Colorado, New Mexico and Nebraska.
Our Wildlife Code continues to protect mountain lions from indiscriminate shooting, but also allows citizens to protect themselves and their property. It states, Mountain lions can be taken year-round when committing or about to commit depredation on any domesticated animal or when deemed an immediate safety hazard. Individuals who kill a mountain lion must immediately call a game warden or other Department employee. The carcass (including hide) will be examined by a Department employee within 24 hours for biological data collection, which may include the removal of a tooth.
Size
The size of these animals varies by sex. Males average seven feet long (from nose to the tip of its tail) and weigh around 140 pounds, while females average six feet in length with a body weight around 95 pounds.
Habitat
Mountain lions prefer dense cover or rocky, rugged terrain, generally in areas of low human habitation, or regions of dense swamps. The size of the home range is typically 50 to 75 square miles for females and 90 to several hundred square miles for males.
How To Observe
If you have evidence of a mountain lion, or a sighting, please REPORT YOUR SIGHTING. The Wildlife Department maintains a list of confirmed sightings.